INTRODUCTION
Everyone would have seen Barcode. It
plays a vital role in all shops while billing the materials or products. Barcode
reader or scanner scans the Barcode labelled on the products. The barcode has
some information about the products. The barcode displays certain information
like item description, price while billing the materials on the computer.
 |
| BARCODE |
WHAT IS A BARCODE?
Barcode is a unique code to the product,
which it represents. Every barcode is unique i.e., all products have unique
barcode all over the World. Barcode
might be in square or rectangular shape. It has set of black parallel lines
(bars) with white spaces with varying width sizes. Barcode represents the data
in visual format.
Barcode is in the form of numbers and lines it easily read by the machine. Barcodes used for quick identification of the commodity.
The barcodes also referred as Universal Product Code (UPC). Barcodes are very useful for maintaining clear and accurate information about the products.
The lines or bars in the barcode represent the binary digits 0 and 1.
The information contains in the barcodes are price, weight, manufactured date, expiry, name of the manufacturer, to track inventory, on invoices to help in accounting and other business related data of that product or item.
What do the number and lines in the barcode meant?
The combinations of numbers and bars varies from companies or manufacturers. The big companies or firms or large manufacturers uses longer numbers. Each numbers in the barcode has specific meaning.
The below barcodes are EAN - 13 Barcodes. India follows EAN-13 barcode.
 |
| EAN - 13 BARCODE |
The barcode has 3 parts namely left guard, centre guard and the right guard.

The information coded in between the bars and the spaces. The scanning device or barcode reader has laser light to identify the code by scanning the lines from left to right. The reader or scanner examines the barcode or pattern and converts the information into machine-readable language i.e., 0’s and 1’s.
The very first number written next to the centre guard in the right hand side notifies about the type of item i.e., the item is made from plastic or some other, vegetarian or non-vegetarian.
If the numbers are 0,1, 6,7,8 : it is standard UPC number.
If the number is 2 : item which is measured by weight e.g. :fruits, vegetables, meat. The price of the item based on weights. The item can be either vegan or non-vegan.
If the number is 3 : the item is related to pharmacy.
If the number is 4 : non edible products.
If the numbers are 5 and 9 : it is for coupon use.
If a barcode printed on the coupon and read, by the scanner, the information of that coupon verified in the computer and the purchase of the item price deducted automatically from the coupon.
The numbers near to the left guard denote the country code. The number can be either 2 or 3 digits.
The next four digits denote manufacturer code or number.
The five digits next to the centre guard bars is the product code.
The last number near to the right guard is the check digit or number. This gives details about whether the scanner has read the barcode correctly.
- Now let us see some of the country codes
- India : 890
- U.S.A and Canada : the numbers from 00 to 13
- France : 30 – 37
- Germany : 40 – 44
- Japan : 45 – 49
- Russia : 46
- Taiwan : 471
- Srilanka : 479
- U.K : 50
- China : 690 -692
TYPES OF BARCODE
There are two types of barcodes.- 1D or 1 Dimensional or Linear Barcodes
- 2D or 2 Dimensional Barcodes
1D OR 1 DIMENSIONAL OR LINEAR BARCODES
A Linear barcode feeds any type of text information. This barcode used generally on usual products like groceries, stationery etc.
Many patterns of 1D use only numerical values for storing information while other patterns use additional alpha or alphanumeric characters.
There are many patterns or designs used in Linear Barcodes for specific purposes. Some of the patterns are :
- CODABAR: CODABAR is an antique design used in libraries and blood banks. CODABAR is no longer in use. However, it is in usage by a few libraries and other organizations. A CODABAR has up to 16 unique numeric characters and an optional four more letters (usually A, B, C, and D). The alpha characters placed at the ends denote where the barcode is in usage like a library, blood banks, photo lab. CODABAR does not have a check number because it is self-check.
 |
| CODABAR |
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons
- CODE 11: CODE11 barcode used in telephones now it is no longer in use.
 |
| CODE 11 BARCODE |
- CODE 39: CODE 39 or ‘Alpha 39’. CODE39 encodes up to 43 alphanumeric characters. CODE 39 is the first barcode to use both numbers and alphabets. CODE 39 generally utilized by the military and automotive industries.
 |
| CODE 39 |
 |
| CODE 3 OF 9 |
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons
- CODE 93: CODE 93 is a modified version of CODE 39. CODE 93 is highly safe and compact. CODE 93 uses additional five characters. CODE 93 is more effective than CODE 39. CODE 93 generally utilized by the military, automotive industries, and Canada Post.
- CODE 128: As the name says, it utilizes 128 ASCII characters such as alphabets, numbers, symbols, punctuations, and many more. CODE 128 stocks more data, implemented in the logistics (purchase, shipping), and other fields.
The sub types of Code 128 are :
Code 128 A: have numeral, upper-case alphabets, and control characters, like tab and new-line.
Code 128 B: have numeral, upper, and lower-case alphabets.
Code 128 C: has a numeral only.
 |
| CODE 128 |
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons
 |
| CODE 128 B |
Code 128 extensively used worldwide in logistics, shipping and packaging industries.
- EAN Barcodes: EAN – European Article Number now renamed as International Article Number.
- EAN - 2: made use for magazines, the last two numbers indicates the volume or month of issue.
 |
| EAN - 2 BARCODE |
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons
- EAN - 8: EAN-8 used for tiny packages like chocolate, cigars, and mini single wrapped items. EAN-8 has 8 digits used by countries other than U.S. and Canada. The 8 digits partitioned into two segments with 4 digits. The two digits indicate the country from where the barcode furnished. Then the five digits indicate the product and the remaining one digit is the check number.
 |
| EAN - 8 BARCODE |
- EAN - 13
 |
| EAN - 13 |
EAN – 13 is equal to the UPC barcode, which is used in U.S. EAN – 13 barcodes generally accepted barcodes in Europe. EAN – 13 operated by supermarkets and other retail firms for the identification of the products. EAN – 13 has 13 digits. The first two numbers denote the country code. The next five-digit indicates the manufacturer code or the brand. Then the five-digit indicate the product code. The last number is the check digit. The check digit gives details about whether the scanner has read the barcode correctly.
- ISBN BARCODE : The International Standard Book Number is a unique numeric code used commercially for identifying books.
 |
| ISBN |
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons
- ISBN with 5 digit Add on : The add on 5 digits used in ISBN graphics. The first barcode is the ISBN barcode and the next barcode with 5 digits implies the price or cost of the book. The first number ‘5’ denotes the currency ‘$’, the next four numbers represents the price of the book. If the price of the book is above $99.99 the barcode used as 5999.
 |
| ISBN WITH ADDON 5 |
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons
In the above barcode, the price of the book is $44.95
- ISMN : The International Standard Music Number is a unique number representing all the music publications worldwide.
 |
| EAN -13 - ISMN |
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons
- LOGMARS : Logistics Applications of Automated Marking and Reading Symbols. LOGMARS operated by the U.S. Department of Defense and is managed by Military Standard MIL-STD-1189B
- MSI-PLESSEY BARCODES : MSI or Modified Plessey barcode. MSI operated chiefly for inventory control, marking storage containers and shelves in warehouse environments.
 |
| MSI - PLESSEY BARCODE |
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons
 | |
|
|
| |
|
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons |
-
PHARMACODE :
PHARMACODE is a Pharmaceutical Binary Code operated by the Pharmaceutical industries for managing the packaging.
 |
| PHARMACODE |
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons
- UPC : Universal Product Code. UPC also referred to as UPC – 12, UPC – A. Uniform Grocery Product Code Council along with IBM designed this code. UPC barcodes comprised of twelve digits, and operated by supermarkets for identifying the products throughout U.S. and Canada.
 |
| UPC - 12 BARCODE |
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons
- UPC – 8 or UPC – E: UPC-8 is a compact form of UPC-12 barcode. UPC-8 operated by all grocery shops in the U.S. for smaller items.
 |
| UPC -8 BARCODE |
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons
Apart from these barcodes there are many patterns used for different scales worldwide.
2D OR 2 DIMENSIONAL BARCODES
This code also known as Matrix Code. The information stored in two-dimensional pattern. Coded both horizontally and vertically and it feeds more information like price, quantity, web address and images. These barcode read using iPhones, android Mobiles and many other devices, which has integrated cameras. There are many types of 2D barcodes designed for particular purposes. Some of them are :
- AR CODE : It is known as Augmented Reality Code. Augmented Reality Code is a type of marker. AR code can have QR code too.
 |
| AR CODE |
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons
- AZTEC CODE : Andrew Longacre developed the AZTEC code. AZTEC code utilizes its space more effectively than any other matrix code. AZTEC Code holds many data in a tiny place, and it has error correction. AZTEC Code operated in hospitals, airline tickets, car registration, and travel.
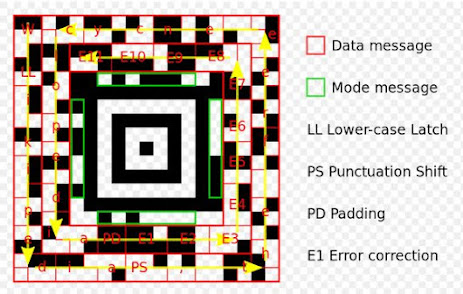 |
| AZTEC CODE |
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons
 |
| AZTEC CODE |
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons
- DATA MATRIX CODES: A data matrix encodes up to 2,335 alphanumeric data or 3116 numerical characters. A Data Matrix code formed of black and white cells organized in a square or rectangle model. A Data Matrix code pattern able to read even if it is 40% damaged because of its inbuilt error correction structure. The Data Matrix code used in aerospace, for labelling the items, defense, and in print media.
 |
| DATA MATRIX CODE |
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons
- DPM CODES : referred as Direct Part Marking. DPM is a method of printing the barcode on the part of the item directly. The purpose of DPM is to track and ensure safety. If the item gets damaged due to fire or any other accidents, the permanent mark on the product reveals the product manufacturer, reason for the accident, etc. Aerospace, automotive, mobile phone manufacturers operate DPM.
 |
| DPM CODE |
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons
- MAXI CODE Maxi code also referred as ‘Bird’s Eye code’ or ‘UPS code’.The Maxi Code examines fast and accurately still on a fast moving conveyor belt. The Maxi Code encodes 93 alphanumeric characters. The Maxi Code has an error correction code. United Parcel Service for tracking and shipping packages use the Maxi code. The Maxi Code has dots instead of bars.
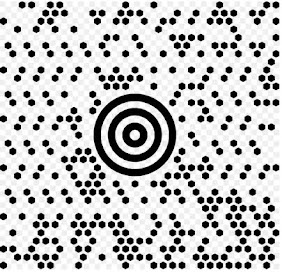 |
| MAXI CODE |
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons
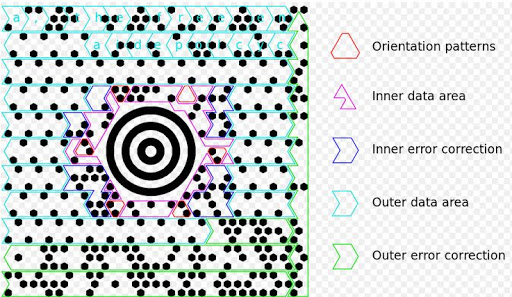 |
| The functional regions of a Maxicode symbol |
- PDF 417: PDF 417 holds huge text and data. PDF 417 is a single barcode comprised of four bars and four spaces, and it is 17 units long hence the name 417. PDF 417 reads 1800 ASCII characters in a single barcode or 1100 binary characters per symbol. PDF 417 operated in driving license, postage, FedEx packages.
 |
| PDF 417 BARCODE WITH FUNCTIONAL REGIONS |
 |
| PDF 417 BARCODE |
- QR CODE : A Quick Read code is a 2D
matrix code.
A QR code is either simple or complex. A QR CODE is a square shape with black and white cells. A QR CODE encodes numeric, alphanumeric characters, binary characters, and Chinese logographic characters. A QR CODE stores much data, and it has built-in error correction for reading when damaged. If the error correction holds a large space, then the low amount of data is stored and vice versa. A QR CODE scanned using smartphones too. A QR CODE is commonly used in advertising to expose the brand.
 |
| QR CODE |
 |
| STRUCTURE OF QR CODE |
CONCLUSION
Barcodes used for variety of purposes and makes the work much easier and error free. There is also negative side. Some people considers barcodes to be an monitoring technology. The book ‘The New Money System 666’ authored by Mary Stewart Relfe represents the number 666 as the ‘Number of the Beast’. Old Believers, a detachment from the Russian Orthodox Church believes barcodes are the signs of the ‘Antichrist’. Phil Donahue, who works as a host in the television labelled barcode as ‘a corporate plot against consumers’.





No comments: