INTRODUCTION
Calcium is a mineral that is indispensable for life because the body requires calcium for developing up sturdy bones and sustaining the bones healthy.
Hypocalcemia and Osteoporosis are the consequence of a lack of calcium in the body. The indications of Hypocalcemia disease are memory loss, confusion, muscle spasms, numbness (in hands, legs, face), the bones fractures easily, weak nails, depression, hallucination, muscle cramps are few of the signs.
Osteoporosis: As seen earlier, bones are a reservoir of calcium, the body is insufficient of calcium and Vitamin D, the body sucks calcium from the bones making the bone weak and porous the bone losses its strength as well as mass.
 |
Osteoporosis |
PARATHYROID GLAND
The parathyroid glands are four glands, which are small and rounded, arranged in two pairs embedded in the thyroid gland. Each Parathyroid gland is tiny, yellow, and smooth. The parathyroid helps the nervous and muscular systems to function efficiently.
 |
| Parathyroid Gland - Green Colour |
Image Source: Wikimedia Commons
These four parathyroid glands found on the backside of the thyroid gland. They are nearly the size and structure of a grain of rice. Parathyroid glands monitor the calcium levels in the body.
HORMONE AND ITS FUNCTIONS
The parathyroid glands discharge parathyroid hormone (PTH) or parathormone. This hormone improves the calcium and phosphorous levels in the blood.
- PTH stimulates the breakdown of bones i.e., the release of calcium from the bones. For this process, PTH triggers Osteoclasts, a type of cell to shatter the bones and for building up bone tissue. These cells breakdown the calcium from the bones and release it to the bloodstream.
- PTH enhances the re-absorption of calcium from the food by making the penetrability of the intestinal membrane. Thus, more calcium absorbed into the bloodstream, and the calcium level increases.
- PTH retains the calcium from the kidneys else, it would expel as urine. PTH orders the kidneys to transform the inactive Vitamin D into the active form. Then passed into the intestine, and calcium retained.
PTH reduces the phosphate levels in the blood serum. Since phosphate forms a salt with calcium when phosphate is released by the kidneys subsequently calcium level increases.
If the calcium level decreases, the PTH brings more calcium and makes the blood calcium level typical, in contrast, if the calcium level raises the parathyroid glands inhibit PTH secretion.
The stability of calcium level in the blood makes the heart, kidneys, nervous system, and bones to function efficiently else, it leads to diseases.
DISORDERS
The high or low level of secretion leads to disorders or diseases.
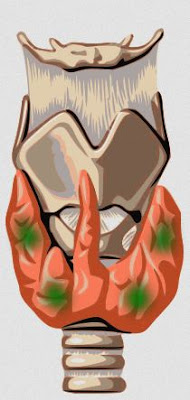
1) Hyperparathyroidism: The PTH secretes an excess amount of calcium, even when the calcium level is typical. At the early stage, it is like growth in the gland without any impairment then becomes parathyroid gland enlargement later it leads to a cancerous tumour. The symptoms are fragile bones, stones in the kidneys, abdominal pain, bone pain, and depression.
 |
| Brown tumours on the hands in a patient with hyperparathyroidism. |
Image Source: Wikimedia Commons
2) Hypoparathyroidism: The PTH secretes an inadequate amount of calcium. Hypoparathyroidism decreases the calcium level in the blood (hypocalcemia) and increases phosphorus levels in the blood (hyperphosphatemia).
Hypoparathyroidism happens because of damage or removal of parathyroid glands during parathyroid or thyroid surgery, extensive radiation treatment, or even low levels of magnesium in the blood.
The body can survive with one parathyroid gland. The removal of all four parathyroid glands leads to a decrease in calcium level within the blood, which is a severe condition.
3) Osteoporosis: This is a condition where one of the parathyroid glands is overactive; it releases too much PTH hormone. Osteoporosis causes the bones to release calcium frequently into the bloodstream.
 |
| Osteoporosis |
CONCLUSION
Mostly all cells in the body utilize calcium for better functioning of the body, which includes the nervous system, muscles, and heart. Calcium is a mineral-rich in milk, cheese, dairy foods, green leaves, nuts, soya beans, soya drinks, bread, or things made up of fortified flour, fish, cabbage, broccoli. Fruits such as Apricots, Kiwi, Oranges, Papaya, Pineapples, Berries, Litchi also have calcium. . Besides these foods, ragi cereal is one of the best sources of calcium. Apart from consuming these foods, avoid consuming caffeine, soft drinks, and alcohol, which reduce calcium



No comments: