GONADS
These are the reproductive organ present in the human body. In the male, it is called ‘Testes’ and in females called ‘Ovary’. Testes produce ‘Sperms’ and Ovary produce ‘Ovum’.
These organs discharge hormones, which play a vital role in the development and functioning of reproductive organs. The pituitary gland controls Gonads.
TESTES OR TESTICLES:
Testes are a couple of sperm-producing oval-shaped organs located in the sac called the scrotum, which is a loose pouch of skin. Testes are visible since they are outside the body behind the penis. Testes require chill surrounding for producing healthy sperms.
SPERMS
Image Source : Wikimedia CommonsSPERM
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons
Hormones of Testes
As testicles produce healthy sperms, it also secretes a hormone called testosterone. The Hypothalamus and Pituitary gland regulate the testes to produce and secrete testosterone. The Hypothalamus indicates the Pituitary gland to discharge gonadotrophic substances. Gonadotrophic substances are present in the follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone.
The Luteinizing hormone (LH) stimulates testosterone production. If too much testosterone secreted, the Hypothalamus signals the pituitary gland to secrete less LH, which in turn signals the testes to decrease the testosterone levels.
Testosterone
This hormone is existing only in male human beings. This hormone is liable for regulating the development of male sex organs and aspects of males like change in voice, growth of muscles, mustache, body hair, and beard.
The testes start secreting this hormone when the boy was a foetus. The secretion continues even after birth and stops during the childhood stage. Then again, it starts secretes by puberty.
DISORDER
Hypogonadism: Hypogonadism condition arises when there is an inadequate of Testosterone secretion. The weakness of bones, infertility, and loss of body hair are the consequences of Hypogonadism. This disorder can be of two-factor one is light and the other is severe. The light factor hit the testicles, and the acute form attacks the pituitary gland, which in turn alters the discharge of testosterone.
OVARIES
Ovaries are reproductive organs present in the females of human beings. Ovaries are two in numbers it produces egg cells. Ovaries are oval-shaped and present on both sides of the uterus. Ovaries secrete two types of hormones.
 |
| Anatomy of the internal structures of the ovary. |
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons
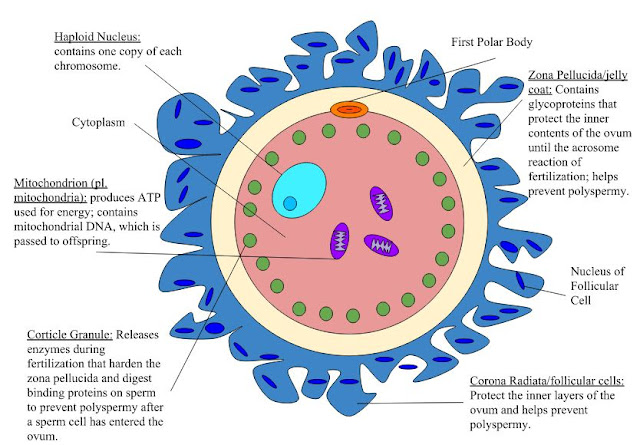 |
| Human ovum |
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons
HORMONES AND FUNCTIONS
Besides producing eggs, ovaries also secrete hormones as being an endocrine gland. These hormones are responsible for the growth of reproductive organs and female characteristics. The hormones are:
(i) (O)Estrogen: This hormone is liable for the development of reproductive organs and feminine traits like voice, soft skin, mammary glands, reproduction, menstruation, menopause, etc.
This hormone has substances like estradiol, estrone, and estriol that work together to form healthy reproductive organs during puberty and fertility. This hormone notifies the pituitary gland to release oxytocin (for the contraction of uterine) during the completion of the pregnancy period.
The ovaries release the ‘relaxin’ hormone to lighten up the pelvic ligaments for labor.
(ii) Progesterone: Corpus luteum, a temporary gland, discharges this hormone once the egg enters the fallopian tube.
The purpose of this hormone is to make the body for pregnancy by inhibiting the contraction of uterine, which may upset the embryo, making the breasts for lactation. Progesterone helps in proper menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
DISORDERS AND TREATMENT
(i) Osteoporosis: The bone-producing cells referred to as osteoblasts, and the bone-eating cells referred to as Osteoclasts. When the secretion of the Oestrogen level, declines osteoblasts do not produce new bones at the same time the Osteoclasts eat the bones. Osteoporosis is related to menopause. The treatment given for Osteoporosis is the replacement of Oestrogen can prevent bones from fractures.
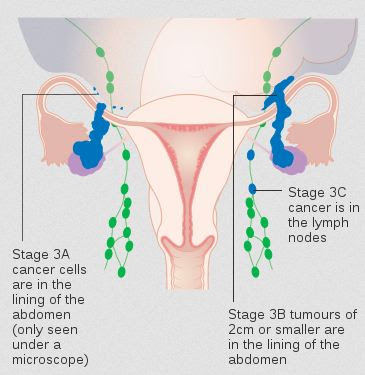
(ii) Ovarian Cancer: This is dangerous, and it is a rare case since it does not show any symptoms at the earlier stages. Only after the formation of cancer cells, it will show some symptoms like continuation abdominal pain, indigestion, bloating, abnormal uterine bleeding, and pain during sexual intercourse.
Image Source : Wikimedia CommonsStage 2A to 2C ovarian cancer
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons Stage 3A to 3C ovarian cancer
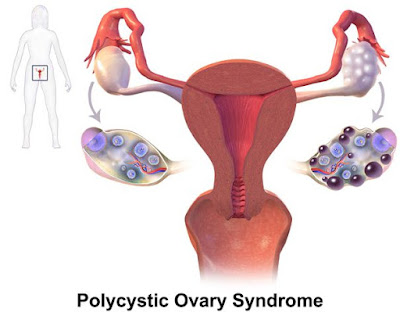
(iii) Ovarian Cysts: Ovarian Cysts can affect women of all ages, particularly women who bear a child. Cysts mean a sac filled with fluid. The size of a cyst can vary from a pea to a big grapefruit. Ovarian Cysts can be of two types. One is Functional cysts, and the other is PCOS.
Image Source : Wikimedia CommonsBenign Ovarian Cyst
- Functional cysts: Functional cysts are usual in the menstrual cycle. It is harmless. After a few menstrual cycles, it vanishes.
- PCOS: The abbreviation is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome or pathological cysts meaning many cysts. PCOS is due to the increasing level of androgens. PCOS causes painful symptoms like irregular menstruation, weight gain, infertility, acne, hair growth in the face and body.
Image Source : Wikimedia Commons








No comments: